 |
 |
 |
 |
|
JANUARY 1942
1 January: In Washington 26 countries signed the "United Nations Pact" which is based on the "Atlantik Charter". 2 January: Japanese troops entered Manilla (Philippines). 4 January: In the U.S. the selling of newly produced private cars was prohibited because the car production should be converted to military vehicles. 7 January 1942: Stutthof officially became a concentration camp under the control of the Inspectorate of Concentration Camps. 10 January: The Rzeszow Ghetto was closed off. 20 January: "Wannsee Conference" in Berlin. 23 January: Jews were no longer allowed to drive a car. Identity cards had to show the letter "J" ("Jew"). 26 January: The first U.S. troops arrived in Europe (North Ireland). 31 January: Einsatzgruppe A reported 229,052 killed Jews. 31 January: Battle of Singapore. Mid-January: Chelmno: The SS started to exterminate the Jews of the Lodz Ghetto. 10 men from the T4 centre Bernburg arrived at Belzec. |
 |
|
FEBRUARY 1942
1 February: The "SS Wirtschafts- und Verwaltungshauptamt" (WVHA) was established. 5 February: Reichsjugendführer Axmann called for a war service of the HJ ("Hitlerjugend" / Hitler Youth). 7 February: The German advance in North Africa was stopped at Tobruk by British troops. 9 February: To save fuel private tours by car were no more allowed in Germany. 11 February: 15 year-old German pupils of high schools were recruited for air defense service ("Luftwaffenhelfer"). 18 February: Singapore surrendered to Japanese troops. 19 February: Japanese air raid on Darwin (Australia). 25 February: The German jurisdiction was adopted in the occupied Baltic States and the Ukraine. Belzec: The construction works were completed. |
 |
|
MARCH 1942
8 March: Japanese forces took New Guinea. 10 March: French troops advanced in Libya. 17 March: 1,400 Jews from the Lublin Ghetto were deported to Belzec. Until 14 April 26,000 Jews from Lublin were deported to Belzec. 17 March: 1,500 Jews from the Lviv Ghetto arrived at Belzec. Until 30 March 15,000 Jews from Lviv were deported to Belzec. 24 March: First deportation from Izbica to Belzec. 24-25 March: Beginning of the deportation transports from Slovakia. 25 March: Jews were forbidden to marry non-Jews. Intercourse with non-Jews was forbidden. 26 March: The first deportation trains arrived at Auschwitz-Birkenau. 27 March: Start of the deportation of French Jews to Auschwitz. 28 March: First area-wide bombing of a big German town, Lübeck, by the Royal Air Force. 31 March: The first deportation from Stanislawow Ghetto (Distrikt Galizien) to Belzec (5,000 Jews). It was one of the biggest transports to Belzec in the first phase of the camp. From March until June 1942 around 27,000 Jews from abroad were deported to the transit ghettos Izbica (17,000 persons), Piaski (5,000 persons), and Rejowiec (5,000 persons). Late March: Bunker 1, the first (primitive) gas chamber at Auschwitz-Birkenau, was put into operation. |
 |
|
APRIL 1942
3-4 April: The first deportation from the Kolomyja Ghetto to Belzec (about 5,000 Jews). 14 April: Great Britain and the U.S. agreed on an invasion of North France in 1943. 18 April: 16 U.S. bombers from the carrier Hornet bombed Tokyo, Yokahama, Kobe, and Nagoya. 20 April: In Germany women were ordered for work in the defence industry. 24 April: In Germany Jews were not allowed to use public transportation. Belzec: Franz Stangl visited the camp for a briefing by Wirth concerning Stangl's duties as commandant at the soon to be opened Sobibor death camp. Belzec: Wirth temporarily closed the camp and left for Berlin. Sobibor: SS-Obersturmführer Franz Stangl was appointed commander of the camp. In mid April Sobibor was ready to receive the first transports. Experimental gassings took place. |
 |
|
MAY 1942
3 May: Every Dutch Jew aged 6 and over was ordered to wear a yellow star on their left breast. 3 May: Japanese troops captured Mandalay (Burma). 5 May: Beginning of the mass deportations from Pulawy County (Lublin District). Until 12 May about 20,000 Jews from this region were deported to Sobibor. 5 May: The Netherlands: A ban on travel was announced. Jews were no more allowed to buy in non-Jewish stores. 7-8 May: Battle of the Coral Sea (Pacific). 12 May: First mass gassing of Jews at Auschwitz-Birkenau. 12 May: Beginning of the mass deportations from Krasnystaw County. Until 15 May about 10,000 Jews from this region were deported to Sobibor. 20 May: British troops left Burma. 21 May: First deportation from Chelm to Sobibor. Until 23 May about 4,300 Jews were deported. 26 May: Mutual assistance pact between Great Britain and the USSR. 27 May: Attack on Heydrich in Prague. 28 May: Battle of Kharkiv (Charkow / Ukraine). 240,000 Soviet soldiers were captured by German troops. 28 May: Mexico declared war on Germany and Italy. 30 May: 1,000 Royal Airforce bombers destroyed the centre of Köln (Germany). Eichmann visited Bratislava (Slovakia) to inspect the progress of the deportations of Jews. Sobibor: Mass exterminations began in the first days of May. Treblinka: The extermination camp was established. Establishment of the last ghettos (in Byelorussia). |
 |
|
JUNE 1942
1 June: Jews in France, Holland, Belgium, Croatia, Slovakia, and Romania were ordered to wear yellow stars. 1 June: Beginning of the deportations from Hrubieszow County. Until 10 June about 12.000 Jews were deported to Sobibor. 3 June: Battle of Sevastopol. 3-6 June: Three trains with 5,000 Jews from Krakow arrived at Belzec. 4 June: Heydrich died in Prague. 4-6 June: Battle of Midway. 5 June: The U.S. declared war on Romania, Hungary and Bulgaria. 5 June: SS report: 97,000 persons have been "processed" in mobile gas vans. 10 June: In retaliation for the assassination on Heydrich the SS destroyed the Czech village Lidice. All male inhabitants older than 15 years were killed. 11 June: Beginning of the deportations from Tarnow Ghetto to Belzec. Until 19 June about 11,500 Jews from Tarnow were deported and hundreds were executed at Zbylitowska Gora near Tarnow. 11 June: Eichmann met representatives from France, Belgium, and Holland to coordinate the deportation of Jews. 11 June: The U.S. and the USSR agreed on mutual cooperation and military assistance. 12 June: Himmler approved the "Generalplan Ost" which intended the resettlement of the Slav population of East Europe to Siberia. 21 June: German troops took Tobruk. 23 June: Mussolini agreed on Rommel's plan to occupy Egypt. 23 June: Viktor Brack wrote to Himmler about sending additional T4 personnel for the "Aktion Reinhard" killing operations due to begin on 1 August. 25 June: General Eisenhower became commander-in-chief of the U.S. troops in Europe. 30 June: At Auschwitz, a second gas chamber (Bunker II) was made operational at Birkenau. All Jews in occupied France were ordered to wear a yellow star. 15-20 gas vans were delivered to the Einsatzgruppen, "operating" in the Soviet Union. |
 |
|
JULY 1942
1 July: German troops occupied Sewastopol (Crimea). 2 July: Jews from Berlin were sent to Terezin (Theresienstadt). 7 July: Himmler granted permission for sterilization experiments at Auschwitz. 14 July: Establishment of a sealed ghetto in Przemysl. 15 July: First deportation train from the Dutch camp Westerbork to Auschwitz. 16 July: Hitler moved his headquarters from East Prussia to Winniza (Ukraine). 16 July: In Paris 12,000 Jews were arrested for deportation and sent to Drancy (near Paris). 17-18 July: Himmler visited Auschwitz-Birkenau for two days, inspecting everything, then promoted Kommandant Höss. 19 July: Himmler visited Trawniki. 19 July: Himmler ordered Krüger (Höherer SS- und Polizeiführer / HSSPF Krakau) and Globocnik (SSPF Lublin) to eliminate the residual Jews of the Generalgouvernement. By 31 December 1942, no Jews were to remain unless they were in the ghettos of Warsaw, Krakow, Czestochowa, Radom, and Lublin (start of Aktion Reinhard). 22 July: Treblinka: The camp was ready to receive transports. 22 July: The "Große Umsiedlungsaktion" ("Great Resettlement Action") in the Warsaw Ghetto started. Destination: Treblinka. In July, 64,606 Jews were deported. 23 July: Treblinka: The extermination programme began, the first train of the "shuttle service" from Warsaw arrived at the station. 23 July: 500 patients of the mental home in Kobierzyn (Poland) were killed by the Nazis. 26 June: The Netherlands: The Jewish Council was notified of forthcoming deportations to the East. 30 June: The Netherlands: The Nazis ordered all Jews off the streets. A night curfew was introduced. Belzec: Additional T4 personnel arrived. Belzec: The new chambers were operational in mid-July. |
 |
|
AUGUST 1942
1 August: SS-Obersturmführer Gottlieb Hering, Wirth’s police comrade for over 20 years, replaced him as Commandant of Belzec. 7 August: U.S. Marines invaded Guadalcanal (Soloman Islands) and started a jungle warfare. 13 August: Start of the Manhattan Project (atomic bomb) in the U.S. 19 August: A first Allied landing operation at Dieppe (Channel Coast / France) failed. 19 August: Wirth visited Treblinka. 20-24 August: Liquidation of the Kielce Ghetto. 26-28 August: 7,000 Jews were arrested in unoccupied France. 27 August: Liquidation of the Siedlce Ghetto. 30 August: The last offensive of the German Africa Corps failed near Al Alamein (Sahara). Treblinka: SS-Obersturmführer Irmfried Eberl was replaced by SS-Obersturmführer Franz Stangl, the former commander of Sobibor. The yellow "Star of David" was introduced in Bulgaria. Wirth was appointed Inspector of the "Aktion Reinhard" death camps at the end of August. Start of deportations of Croatian Jews to Auschwitz. Auschwitz-Birkenau: Construction works on Crematory II began. |
 |
|
SEPTEMBER 1942
6 September: The last phase of the "Great Action" in Warsaw opened. 9 September: Open pit burning of 107,000 corpses began at Auschwitz in place of burial to prevent fouling of ground water. 12 September: On the Atlantic Ocean a German submarine sank the British troop ship "Laconia". 1,800 Italian POWs were drowned. 16 September: Adolf Eichmann and Rudolf Höß visited Chelmno. 18 September: Reduction of food rations for Jews in Germany. 22 September: The Czestochowa Ghetto clearing started. It ended on 8 October. 24 September: SS-Untersturmführer Karl Brandt proclaimed the end of the resettlement action in the Warsaw Ghetto. Treblinka: Stangl introduced a permanent command of Jewish prisoners. Decision to build new Gas Chambers with ten killing rooms. Höss visited Chelmno and Treblinka. |
 |
|
OCTOBER 1942
1 October: The Jews in German KZs were deported to Auschwitz for extermination. 3 October: First successful launch of the A4 rocket (later called "V2") at Peenemünde (Germany). 5 October: Himmler ordered all Jews in German KZs to be sent to Auschwitz or Majdanek. 12 October: In Italy the selling of toys was prohibited because the industry was ordered to concentrate on war production. 20 October: Germans were called for collecting beech nuts for cooking oil production. 22 October: The SS guards at KZ Sachsenhausen put down a revolt by a group of Jews about to be sent to Auschwitz. 24 October: The battle of El Alamein began. Belzec: According to Reder, Himmler visited the camp. Amon Göth, (later commandant of Plaszow) came to Poniatowa and started to organize a work camp for Jews. On the end of October, a consultation of Jewish underground organizations was held at the Ha-Shomer Hazair headquarters at 61 Mila Street in Warsaw. A ZOB command was formed, to defeat the Warsaw Ghetto, and to teach the Jewish Police and workshop owners a lesson. |
 |
|
NOVEMBER 1942
4 November: Rommel ordered the retreat of his troops from Al Alamein, against Hitler's order. 8 November: Allied landing operation in Northwest Africa ("Operation Torch"). 10 November: German troops occupied Stalingrad. 11 November: German troops occupied the "free" South France, ruled by the "Vichy Government". 13 November: Tobruk occupied by British troops. 22 November: The German 6th Army was encircled by Soviet troops in Stalingrad. 23 November: First systematic air raid of British bombers on Berlin. 26 November: 795 Norwegian Jews were deported to KZ Auschwitz. A similar number safely reached Sweden before the action. 25 of the deported Jews survived the war. Belzec: Pyres for burning the corpses were constructed and were in continual use from early November until March 1943. Mass killing of 170,000 Jews in the Bialystok area. |
 |
|
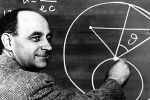
DECEMBER 1942
1 December: Mussolini asked Hitler for ending the war against the USSR. 2 December: First controlled nuclear chain reaction, carried out by Enrico Fermi in Chicago. 4 December: U.S. air raid on Napoli (Italy). 7 December: In the Ruhr (Ruhrgebiet / Germany) the Gestapo arrested most members of the youth resistance group "Edelweißpiraten" (Edelweiß Pirates). 10 December: The first transport of Jews from Germany arrived at Auschwitz. 11 December: The last transport of Jews arrived at Belzec. 15 December: In Italy public schools were closed until mid-February because of lack of fuel. 28 December: German troops retreated from the Caucasus. 28 December: Sterilization experiments on women at Birkenau began. Wirth was given the responsibility of managing and continuing the construction of the DAW (Deutsche Ausrüstungswerke / German Equipment Works), slave labour camps in the Lublin district. Treblinka: On Christmas, Stangl ordered the construction of a fake railway station. |
 |
© ARC 2006